Mini Dose Glucagon for Preventing Hypoglycemia

MINI DOSE GLUCAGON FOR PREVENTING HYPOGLYCEMIA
Everyone may or may not of had the experience where they where not able to fully tolerate a meal due to a little stomach bug, and they find that their blood sugars keep going down. Due to the stomach illness, they are unable to keep down any liquids or solids. The younger the age, usually the more difficulty in ‘encouraging’ feeds at this critical time.
When these levels continue to drop and the child is unable to take anything orally, parents often resort to taking their child to the Emergency Room for intravenous glucose. This can be both traumatic for the child as well as the parents. One strategy to help treat hypoglycemia during these times and prevent a visit to the Emergency Room is to use very small (mini) doses of glucagon; given with a regular insulin syringe, rather than the much larger dose normally given to treat serious hypoglycemia. Clinical studies show that the mini-doses of glucagon raised the blood glucose levels approximately 54-90 mg/dl within the first 30 minutes, and the effect lasted approximately one hour. The glucagon used in these smaller doses did not increase the nausea or vomiting that is commonly associated with the larger dose.
It is important to note that while this option works well during stomach illnesses, it is NOT effective for a severe low blood sugars which would require the full dose of glucagon. However, it may be used if the child refuses to eat or is unable to eat anything after they have received insulin, and the blood sugar is dropping.
WHAT YOU WILL NEED:
- glucagon for injection
- a regular 30-, 50-, or 100-unit insulin syringe
- blood glucose meter and strips
PROCEDURE:
- Reconstitute the glucagon as shown below:
Remove the flip-off seal from the bottle of glucagon. Wipe rubber stopper on bottle with alcohol swab.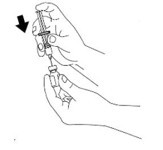
- Remove the needle protector from the syringe, and inject the entire contents of the syringe into the bottle of glucagon. DO NOT REMOVE THE PLASTIC CLIP FROM THE SYRINGE. Remove syringe form the bottle.
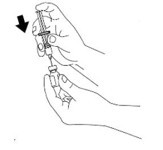
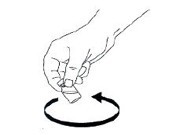
- Swirl bottle gently until glucagon dissolves completely GLUCAGON SHOULD NOT BE USED UNLESS THE SOLUTION IS CLEAR AND OF A WATER-LIKE CONSISTENCY.
- Draw up the recommended dose into an insulin syringe. Each “unit” on the syringe will equal 10 µg (micrograms).
Dose: 2 years and under: give 2 units (=20 µg)
3-15 years: give 1 unit per year of age
Over 15 years: give 15 units (=150 µg) - Inject the mini-dose glucagon exactly as you would insulin (subcutaneously)
- Check the blood glucose every 30 minutes.
- If after 30 minutes the blood glucose levels have not improved (that is, they remain under 80 mg/dL), then repeat the glucagon using double the dose.
- Double Dose: 2 years and under: give 4 units (=40 µg)
3-15 years: give 2 units per year of age
over 15 years: give 30 units (= 300 µg) - The effective dose may be repeated every hour as needed to keep blood glucose levels above 80 mg/dL.
- Give the standard full dose of glucagon if the child has any of the following:
-seizure
-loss of consciousness - Page the diabetes doctor on call or call 911 if you are unable to maintain the blood glucose above 70 mg/dL with food and liquids or with the mini-dose glucagon.
- Reconstituted glucagon should be kept in the fridge between doses, and then discarded after 24 hours.
- Remember to replenish the glucagon as soon as possible! Many pharmacies do not stock glucagon and may need to order it.



